When we hear “thyroid,” we tend to think of “hormones.” We know that hormonal imbalances can cause all sorts of problems in our body, including our sexual health. But is there a connection between the thyroid and erectile dysfunction? This article discusses how thyroid complications impair your erectile strength.
The Thyroid and Your Metabolism
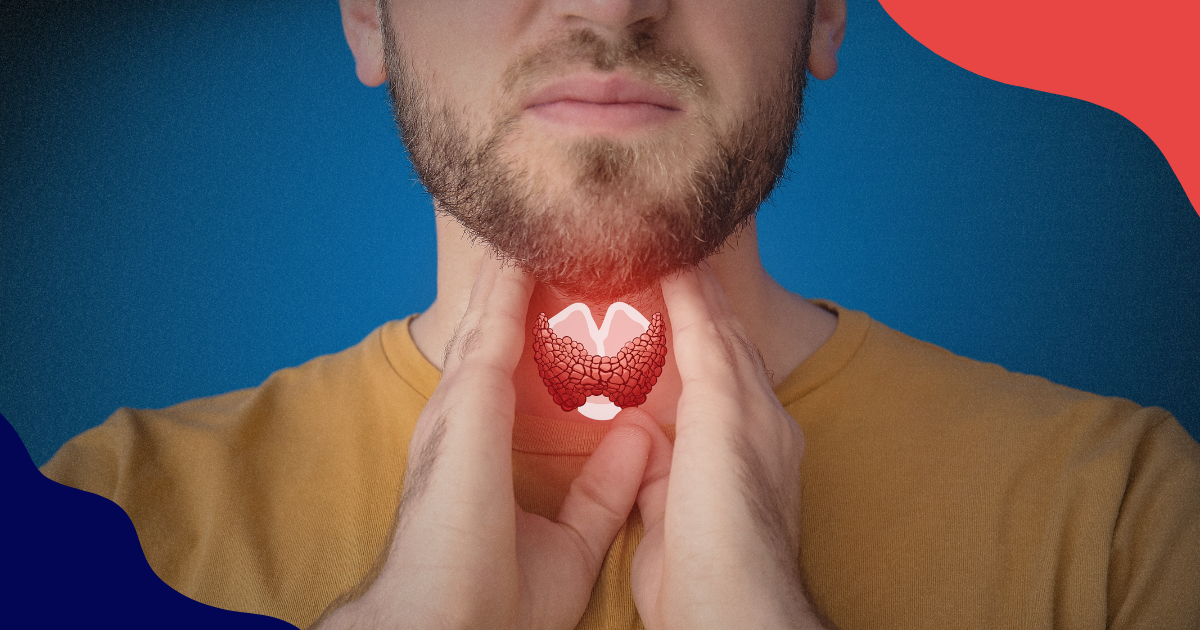
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland in your neck that’s about two inches long. It’s part of the endocrine system, a group of glands and organs that release hormones which instruct various processes in your body. The thyroid specifically controls the speed of your metabolism. Can the thyroid cause erectile dysfunction? Yes, it can if it has any abnormalities, whether within itself or from the pituitary gland and hypothalamus.
When we hear about metabolism, we often think about weight gain. This is because metabolism is responsible for how the body breaks down energy, which we derive from food. But metabolism also governs the distribution of energy and initiates other processes. For example, if you’re not properly processing glucose, you may develop diabetes which can lead to erectile dysfunction due to blood vessel and nerve damage. There’s also the metabolic syndrome, a group of hormonal biomarkers that raise your risk for chronic diseases, both of which can result in erectile struggles.
The thyroid also affects your blood pressure, gut health, temperature regulation, breathing, fertility, and healing. Not only can these impact your erection, but any irregularities also tend to negatively affect your entire sexual health. Testosterone, a hormone crucial for male sexual function, is also produced by the endocrine system. Often, when you have a problem with one part of the endocrine system, it affects the rest due to hormonal imbalance.
Thyroid Diseases Linked to Erectile Dysfunction
We know that the thyroid affects virtually all other systems in your body, which means problems can start in other places, such as the testes and pancreas. But if what you meant by “can thyroid problems cause erectile dysfunction” refers to thyroid diseases, the answer is still yes. Here are the thyroid disorders that raise your risk of erectile dysfunction:
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism occurs when you have an underactive thyroid. This means your thyroid isn’t producing enough hormones called T3 and T4. Symptoms of hypothyroidism include low blood pressure, weight gain, depression, fatigue, sensitivity to cold, and dry skin. Weight gain can manifest as general obesity or excess belly fat which raises your risk of contracting erectile issues. Weight gain and depression alone can lead to erectile dysfunction. Research has also shown that most men with hypothyroidism suffer from erectile dysfunction.
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is the opposite of hypothyroidism. This means you have an overactive thyroid instead. Some studies found that men with hyperthyroidism also have a raised risk of erectile dysfunction though they it may be lower compared to men diagnosed with hypothyroidism. However, hyperthyroidism causes high blood pressure due to a faster heart rate, insomnia, and anxiety, which can independently contribute to erectile difficulties.
Goitre
Goitre is the term for an enlarged thyroid. Normally, you can’t see or even feel your thyroid. Men with goitre tend to have a visible bulge on their neck. They may also struggle to swallow or have a hoarse-sounding voice. Goitre can be caused by hypothyroidism or an infection. In hypothyroidism, the thyroid swells in an attempt to compensate for the deficit in hormone production. Most goitre cases are due to a lack of iodine. Iodine is the nutrient that the thyroid converts into T3 and T4.
Thyroiditis
Thyroiditis is inflammation of the thyroid. It can be due to an autoimmune disorder like Hashimoto’s disease, which is genetic or congenital. With an autoimmune disorder, your immune system mistakenly attacks the cells in your thyroid. Thyroiditis can also be acquired due to an infection or as a side effect of medication or cancer treatment. Thyroiditis can trigger both hyperthyroidism and goitre.
Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer occurs when there is abnormal cellular growth in your thyroid. Your risk of thyroid cancer increases if you have any thyroid disease, obesity, iodine deficiency, or have undergone radiation therapy near the thyroid. But the reverse is also true—if you have thyroid cancer, you’re more likely to develop other thyroid issues. Fortunately, most cases of thyroid cancer respond well to treatment. Untreated thyroid cancer may spread and trigger other types of cancer.
Managing Thyroid Issues and Erectile Dysfunction
If you’re suspecting that you have a thyroid condition and that your erectile dysfunction may be because of it, follow these steps to strategically address both issues:
#1: Get tested for endocrine issues
Your first step would be to consult an endocrinologist, who would refer you for a blood test to check your TSH, T3, and T4 levels. Endocrinologists are doctors who specialise in endocrine problems like thyroid diseases. Note that you should also get a laboratory test for other endocrine disorders, such as low testosterone and diabetes, if you have erectile dysfunction. Endocrine diseases tend to share symptoms, and you may have more than one hormonal imbalance.
#2: Watch your iodine intake
If you’re over 18 years old, make sure you’re consuming around 150 µg of iodine every day. An easy way to incorporate iodine into your diet is by using iodised salt. But you can also get iodine from dairy products and seafood. While it’s more common to struggle with low iodine, you may also experience hyperthyroidism if you’re consuming too much iodine, so stick within the recommended daily intake. Don’t rely purely on salt either—too much salt can lead to kidney issues, which can also cause erectile dysfunction.
#3: Eat a variety of whole foods
The trick to remaining healthy is to eat a balanced diet. This is easier said than done, however. The best way to achieve a balanced diet is to stick to whole or unprocessed ingredients and eat from different food groups (e.g., vegetables, fruits, dairy, meat, seafood). You can also consult a dietitian to find out what diet is best for your specific needs. We have nutritionists and dietitians at the Men’s Health Clinic to ensure our patients are eating the right kinds of food to combat sexual dysfunction.
#4: Practise good sleep hygiene
One common way people disrupt their hormonal balance is by not sleeping properly. Good sleep consists of 7–9 hours of uninterrupted rest at night. If you’re constantly staying up late or being woken up in the middle of the night, you’ll likely feel tired and grumpy when you wake up. To fix your sleep, you must practise good sleep hygiene:
- Don’t consume caffeine in the afternoon onwards
- Avoid stimulating activities in the evening
- Wind down at least 30 minutes before bedtime
- Keep electronics out of reach
- Sleep in a dark and cool room
- Wake up at the same time every day
- Don’t pressure yourself to fall asleep
#5: Manage your stress
Stress is one of the biggest triggers and catalysts of diseases. We talked about sleep earlier—if you don’t get enough sleep, your cortisol (stress hormone) levels increase. Meanwhile, your testosterone levels, which should peak in the morning, end up being low. Cortisol tends to suppress hormone production. Keeping your stress managed through meditation and yoga will prevent cortisol spikes that disrupt your endocrine system. Yoga may also improve your erections through stronger pelvic control and improved circulation.
#6: Reduce hormone-interfering substances
Alcohol, nicotine, and caffeine are the most common substances that disrupt hormonal balance. Cigarettes and alcohol have also been linked to erectile dysfunction. But chemicals don’t only come from what you eat or drink—they can also be found in other products, such as pesticides, cosmetics, and cleaning products. You may not be able to eliminate every single endocrine disruptor, but you can reduce your use of non-essential products that could be harmful.
#7: Maintain regular physical activity
Exercise keeps your muscles and bones healthy. It also strengthens your heart and helps you process cortisol more efficiently. Studies have also found that certain forms of exercise increase testosterone levels over time. While exercise alone usually isn’t enough for weight loss, it will help you maintain weight by burning some calories and stimulating your metabolism. Make sure to get at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week and to move regularly to avoid becoming sedentary.
#8: Get comprehensive care for ED
Even if you’re being treated by an endocrinologist for a thyroid disease, you may still experience persistent weak erections if you have other triggers for erectile dysfunction. Erectile dysfunction can also stem from other causes, such as cardiovascular disease, atherosclerosis, kidney disease, liver disease, cancer, sexually transmitted infections (STIs), mental health disorders, medications, and inflammation. To restore your erectile health, you must address every single trigger, which is what comprehensive care does.
Conclusion
Can thyroid problems cause erectile dysfunction? Yes, hormonal disturbances caused by thyroid issues can impede your erectile health. We recommend speaking to an endocrinologist to find the best treatment for your thyroid issues. As for erectile dysfunction, we have a dedicated team of experts with a proven track record of rehabilitating male sexual dysfunction. Book an appointment to begin restoring your sexual capacity today!




